NEWS | Uzbekistan: the newest member of the GSP+ arrangement
On 10th April 2021, Uzbekistan joined the group of GSP+ beneficiaries, becoming the ninth country to participate in the special incentive arrangement for sustainable development and good governance. Through the GSP+, Uzbekistan will receive duty-free access to the EU market for about 66% of tariff lines. At the same time, the GSP+ supports Uzbekistan in implementing sustainable development objectives and making further progress in the fields of human and labour rights, environmental and climate protection and good governance.

The modern GSP categorises three tiers of tariff preferences and commitments based on a beneficiary country’s level of development. The Everything But Arms (EBA) is a special arrangement for least developed countries which allows duty-free and quota-free access for all products originating in these countries except for arms and ammunition. Under the standard GSP arrangement, lower and lower-middle income countries receive duty reductions on 66% of tariff lines imported into the EU. On top of this arrangement, the GSP+ provides the incentive for vulnerable developing countries to benefit from zero duties on 66% of tariff lines contingent on the implementation of core human rights, labour, governance, and other sustainable development conventions.
In 2019, goods worth €93.79 million were imported from Uzbekistan using GSP preferences, equalling a share of about 40% of overall imports from Uzbekistan. Uzbekistan’s preference utilisation rate most recently stood at 87%, indicating that the Central Asian beneficiary made good use of the preferences granted by the GSP. The product sections that take most advantage of the reduced tariffs are textiles and clothing, plastic articles, as well as fruits, nuts, and vegetables, indicating that Uzbekistan’s export structure is already more diverse compared to its Central Asian neighbours.
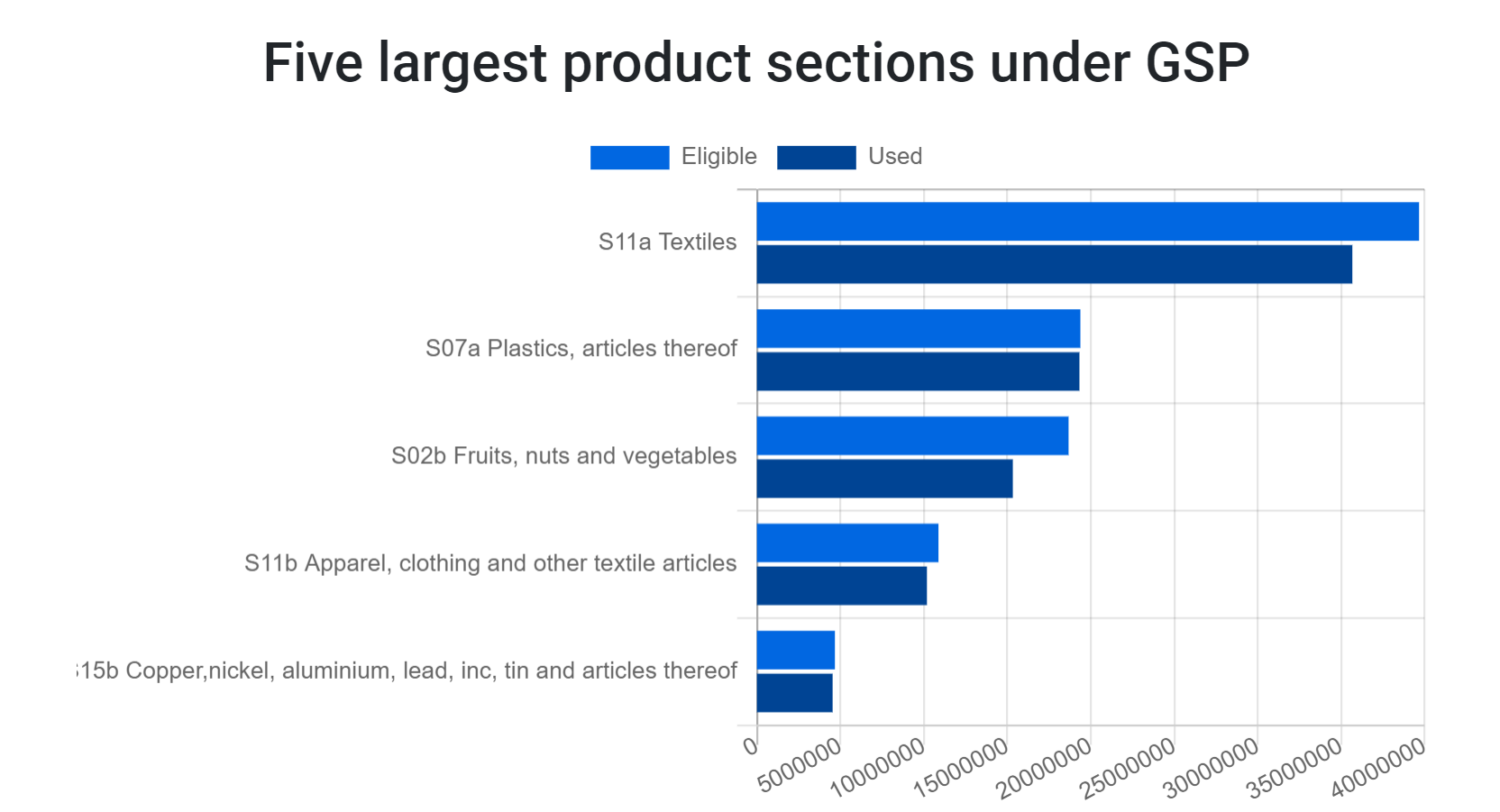
The GSP+ scheme offers additional opportunities to boost trade between the EU and Uzbekistan as tariffs for a number of important export goods, such as woven fabrics, clothing, and articles of plastics, will be removed. Despite relative proximity to the EU market, the trade potential has not yet been fully exploited as the EU only ranks seventh in the list of Uzbekistan’s export destinations.
| Table 1: Uzbekistan- Prominent export articles to the EU market | ||||
| Product name | HS Code | Third country duty | GSP | GSP+ |
| Plastics and articles thereof | 39012090 | 6.5% | 3% | 0% |
| Woven fabrics of cotton | 520812 | 8% | 6.4% | 0% |
| Cotton yarn | e.g. 520523 | 4% | 3.2% | 0% |
| Shelled almonds | 08021290 | 3.5% | 0% | 0% |
| Dried grapes | 080620 | 2.4% | 0% | 0% |
| Molybdenum and articles thereof, including waste and scrap (base metals) | 810299 | 7.00% | 2.4% | 0% |
| T-shirts, singlets and other vests, knitted or crocheted | 610910 | 12.00% | 9.60% | 0% |
Sources: ITC Trade Map and Access2Markets database | ||||
Next to the tangible economic benefits, the GSP+ aims to support beneficiary countries on their path to sustainable development. Under the GSP+ scheme, Uzbekistan will have to present progress in implementing the 27 core conventions which is supported by the EU monitoring process. Through the accession to the GSP+, Uzbekistan commits to close dialogue and exchange with the European Union on human and labour rights, environmental protection and good governance. In recent years, Uzbekistan showed substantial efforts in addressing human and labour rights concerns. According to the ILO, Uzbekistan has made significant progress in the last few years with respect to the elimination of forced labour and child labour, especially in the context of cotton harvests.
For more information on the GSP+ and Uzbekistan, please visit the Uzbekistan country page and the GSP Hub monitoring database. We invite you to leave your comments on Uzbekistan’s participation in the GSP+ using the conversations tool at the bottom of the page. Click on a topic and type your comment in the text box to start a conversation.
More information on Uzbekistan's GSP+ accession